function MO_Animate(varargin)
% This function generates objective space images showing why
% sum-weighted optimizer can not find all non-dominated
% solutions for non convex objective spaces in multi-ojective
% optimization
%
% Guillaume JACQUENOT
if nargin == 0
% Simu = 'Convex';
Simu = 'NonConvex';
save_pictures = true;
interpreter = 'none';
end
switch Simu
case 'NonConvex'
a = 0.1;
b = 3;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
case 'Convex'
a = 0.2;
b = 1;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
end
[X,Y] = meshgrid( 0:stepX:1,-2:stepY:2);
F1 = X;
F2 = 1+Y.^2-X-a*sin(b*pi*X);
figure;
grid on;
hold on;
box on;
axis square;
set(gca,'xtick',0:0.2:1);
set(gca,'ytick',0:0.2:1);
Ttr = get(gca,'XTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'XTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
Ttr = get(gca,'YTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'YTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
if strcmp(interpreter,'none')
xlabel('f1','Interpreter','none');
ylabel('f2','Interpreter','none','rotation',0);
else
xlabel('f_1','Interpreter','Tex');
ylabel('f_2','Interpreter','Tex','rotation',0);
end
set(gcf,'Units','centimeters')
set(gcf,'OuterPosition',[3 3 3+6 3+6])
set(gcf,'PaperPositionMode','auto')
[minF2,minF2_index] = min(F2);
minF2_index = minF2_index + (0:numel(minF2_index)-1)*size(X,1);
O1 = F1(minF2_index)';
O2 = minF2';
[pF,Pareto]=prtp([O1,O2]);
fill([O1( Pareto);1],[O2( Pareto);1],repmat(0.95,1,3));
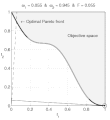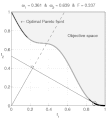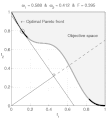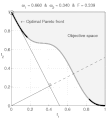
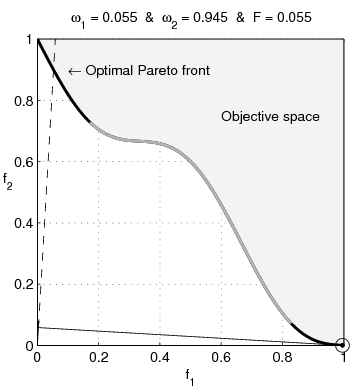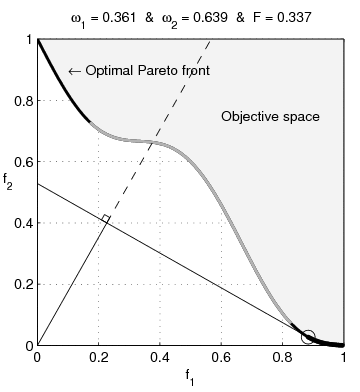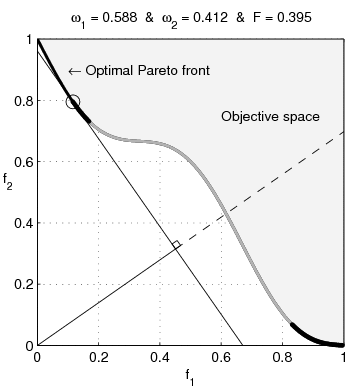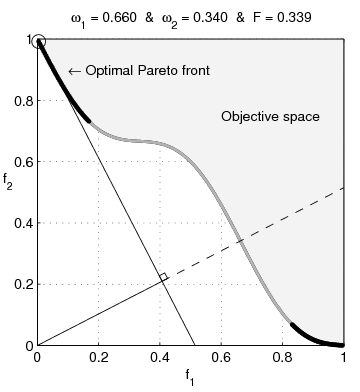
text(0.45,0.75,'Objective space');
text(0.1,0.9,'\leftarrow Optimal Pareto front','Interpreter','TeX');
plot(O1( Pareto),O2( Pareto),'k-','LineWidth',2);
plot(O1(~Pareto),O2(~Pareto),'.','color',[1 1 1]*0.8);
V1 = O1( Pareto); V1 = V1(end:-1:1);
V2 = O2( Pareto); V2 = V2(end:-1:1);
O1P = O1( Pareto);
O2P = O2( Pareto);
O1PC = [O1P;max(O1P)];
O2PC = [O2P;max(O2P)];
ConvH = convhull(O1PC,O2PC);
ConvH(ConvH==numel(O2PC))=[];
c = setdiff(1:numel(O1P), ConvH);
% Non convex
O1PNC = O1PC(c);
[temp, I1] = min(O1PNC);
[temp, I2] = max(O1PNC);
if ~isempty(I1) && ~isempty(I2)
plot(O1PC(c),O2PC(c),'-','color',[1 1 1]*0.7,'LineWidth',2);
end
p1 = (V2(1)-V2(2))/(V1(1)-V1(2));
hp = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(1))+V2(1) p1*(1-V1(1))+V2(1)]);
delete(hp);
Histo_X = [];
Histo_Y = [];
coeff = 0.02;
Sq1 = coeff *[0 1 1 0 0;0 0 1 1 0];
compt = 1;
for i = 2:1:length(V1)-1
if ismember(i,ConvH)
p1 = (V2(i+1)-V2(i-1))/(V1(i+1)-V1(i-1));
x_inter = 1/(1+p1^2)*(p1^2*V1(i)-p1*V2(i));
hp1 = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(i))+V2(i) p1*(1-V1(i))+V2(i)],'k');
% hp2 = plot([x_inter],[-x_inter/p1],'k','Marker','.','MarkerSize',8)
hp3 = plot([0 x_inter],[0 -x_inter/p1],'k-');
hp4 = plot([x_inter 1],[-x_inter/p1 -1/p1],'k--');
hp5 = plot(V1(i),V2(i),'ko','MarkerSize',10);
% Plot the square for perpendicular lines
alpha = atan(-1/p1);
Mrot = [cos(alpha) -sin(alpha);sin(alpha) cos(alpha)];
Sq_plot = repmat([x_inter;-x_inter/p1],1,5) + Mrot * Sq1;
hp7 = plot(Sq_plot(1,:),Sq_plot(2,:),'k-');
Histo_X = [Histo_X V1(i)];
Histo_Y = [Histo_Y V2(i)];
hp6 = plot(Histo_X,Histo_Y,'k.','MarkerSize',10);
w1 = p1/(p1-1);
w2 = 1-w1;
Fweight_sum = V1(i)*w1+w2*V2(i);
Fweight_sum = floor(1e3*Fweight_sum )/1e3;
w1 = floor(1000*w1)/1e3;
str1 = sprintf('%.3f',w1);
str2 = sprintf('%.3f',1-w1);
str3 = sprintf('%.3f',Fweight_sum);
if (strcmp(str1,'0.500')||strcmp(str1,'0,500')) && strcmp(Simu,'NonConvex')
disp('Two solutions');
end
title(['\omega_1 = ' str1 ' & \omega_2 = ' str2 ' & F = ' str3],'Interpreter','TeX');
axis([0 1 0 1]);
file = ['Frame' num2str(1000+compt)];
if save_pictures
saveas(gcf, file, 'epsc');
end
compt = compt +1;
pause(0.001);
delete(hp1);
delete(hp3);
delete(hp4);
delete(hp5);
delete(hp6);
delete(hp7);
end
end
disp(['Number of frames :' num2str(length(V1))]);
return;
function [A varargout]=prtp(B)
% Let Fi(X), i=1...n, are objective functions
% for minimization.
% A point X* is said to be Pareto optimal one
% if there is no X such that Fi(X)<=Fi(X*) for
% all i=1...n, with at least one strict inequality.
% A=prtp(B),
% B - m x n input matrix: B=
% [F1(X1) F2(X1) ... Fn(X1);
% F1(X2) F2(X2) ... Fn(X2);
% .......................
% F1(Xm) F2(Xm) ... Fn(Xm)]
% A - an output matrix with rows which are Pareto
% points (rows) of input matrix B.
% [A,b]=prtp(B). b is a vector which contains serial
% numbers of matrix B Pareto points (rows).
% Example.
% B=[0 1 2; 1 2 3; 3 2 1; 4 0 2; 2 2 1;...
% 1 1 2; 2 1 1; 0 2 2];
% [A b]=prtp(B)
% A =
% 0 1 2
% 4 0 2
% 2 2 1
% b =
% 1 4 7
A=[]; varargout{1}=[];
sz1=size(B,1);
jj=0; kk(sz1)=0;
c(sz1,size(B,2))=0;
bb=c;
for k=1:sz1
j=0;
ak=B(k,:);
for i=1:sz1
if i~=k
j=j+1;
bb(j,:)=ak-B(i,:);
end
end
if any(bb(1:j,:)'<0)
jj=jj+1;
c(jj,:)=ak;
kk(jj)=k;
end
end
if jj
A=c(1:jj,:);
varargout{1}=kk(1:jj);
else
warning([mfilename ':w0'],...
'There are no Pareto points. The result is an empty matrix.')
end
return;
![]() אין בוויקיפדיה דפים המשתמשים בקובץ זה.
אין בוויקיפדיה דפים המשתמשים בקובץ זה.














![{\displaystyle \omega _{1}\in [0;1]~}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/99c8913e84daf282e85b04849cc18cc14594dda7)

